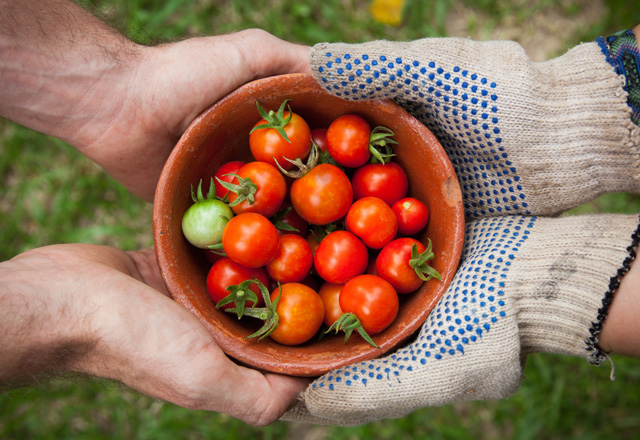
Most of us have seen fair trade products like coffee, bananas, tea, and chocolate during our shopping escapades. But what is fair trade? Very few people know the meaning and function of fair trade in the global economy. Learning how to live a sustainable lifestyle with ethical consumption is practically impossible without understanding fair trade.

Fairtrade has numerous benefits beyond paying food producers more money and establishing a fair compensation plan for workers. This article is the ultimate guide to understanding the meaning, examples, facts, reasons, roles, and challenges behind the concept of fair trade. Keep on reading to learn deep insights into the application of fair trade as a solution to contemporary problems.
What is fair trade?
So, what is fair trade? The meaning of fair trade can vary depending on how each stakeholder perceives its role in benefiting them. In a general sense, fair trade is a quality control system that aims to establish equitable and sustainable trade relationships between agricultural producers in developing countries and the rest of the global economy.
Workers and farmers in such countries understand fair trade as a vehicle through which they can achieve better working conditions and higher compensation. For consumers, fair trade is a way of accessing high-quality and ethical products while supporting farmers to achieve equality in the global business environment. With such equality, we can foster climate-friendly agricultural methods and the development of women in commercial leadership.

Although fair trade is commonly applied in food production, it can also cover other products in developing nations’ domestic markets, like handicrafts, gold, and flowers. Organizations that label such products define fair trade as an integrity and dialogue-based commercial partnership seeking greater fair play in universal trade.
Examples and facts
The existence of fair trade for the last two and a half decades has not stopped many people from developing myths and misconceptions about it. Let us examine a few facts and examples that can debunk such myths.
Fact One – What is Fair Trade vs. Fairtrade International?
There is a vast difference between Fair Trade and Fairtrade International. Fair Trade is the equitable concept of promoting sustainable living through better international trading conditions. Such conditions include higher wages, elimination of child labor, upholding human rights, and gender equality. On the other hand, Fairtrade International is a non-governmental organization that provides certification to farmers from developing countries to help market their products.
Fact Two- Fairtrade Producers
There are various Fairtrade production stakeholders, including producer organizations, workers, and farmers. Globally, there are 1707 producer organizations, with a country distribution of 38%. Such organizations receive a Fairtrade monetary premium that enables them to fulfill various functions, including servicing farmers, training, purchasing agricultural equipment, and housing improvements.

Workers and farmers in the Fairtrade system are about 1.7 million, with 25% being women. On average, each Fairtrade farmer has 5 hectares of land to grow their produce. Fairtrade farmers follow specific ways to be sustainable in production. Such ways include soil improvement, pest management, using harmless chemicals, protecting biodiversity, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
One of the best examples of optimal Fairtrade production is Divine Chocolate. This agricultural company which started as a cooperative is moving mountains in the global chocolate market by facilitating Fairtrade through women empowerment and advocating against child labor.
Fact Three- Fairtrade and UK consumers
Since its inception, The UK has been a significant supporter of Fair Trade, contributing an estimated 1 billion euros in sales premiums. Currently, over 80% of UK shoppers believe in the intention, certification, and production mechanisms resident in the Fair Trade system. Shopping statistics reflect this belief, with 25% of UK shoppers purchasing Fair Trade products regularly.
Why is fair trade important?
Learning how to live sustainably is impossible without understanding the importance of fair trade. Fair trade is vital in combatting the harsh effects of unfair and unethical commercial practices on the international scene. Through fair trade, farmers can receive fair monetary compensation for their produce, enabling them to feed their families and pay fair wages to their workers.
What is its role in the current state of the environment
Economic Role
One of the economic roles of Fairtrade is supporting farmers by establishing a minimum price through which they can sell their produce profitably. Fairtrade organizations also empower farmers to establish cooperative societies that give them better bargaining power within their products’ supply chain. Other economic roles of fair trade in the current state of the environment include improving access to farming services and supporting better agricultural methods.

Environmental Role
Fairtrade contributes to environmental and climatic care by establishing standards that address critical areas like green energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, eliminating GMO products, waste management, and protecting biodiversity. Such standards grant training to farmers on switching to agricultural practices that increase nutrient quality in soils and reduce pets.
Social Role
Fair trade contributes socially to farmers by encouraging them to learn and voice their rights through collective bargaining when negotiating for better working conditions. Fairtrade standards also advocate for the investment of premiums into gender equality, education, and the provision of social amenities to workers. Such investment is essential in improving life quality in rural areas.
How can we solve problems related to this
There are numerous problems related to fair trade, including costly certification, expensive products, poor distribution of administrative fees, and limited success. The best way to solve such problems is to eliminate the unethical practices that prevent fair trade gains from directly impacting the producers.
Conclusion
Improving the global quality of life is the responsibility of all universal citizens. We can all work together to achieve sustainable living by investing in fair trade products that improve our world’s economic, social, and environmental well-being.